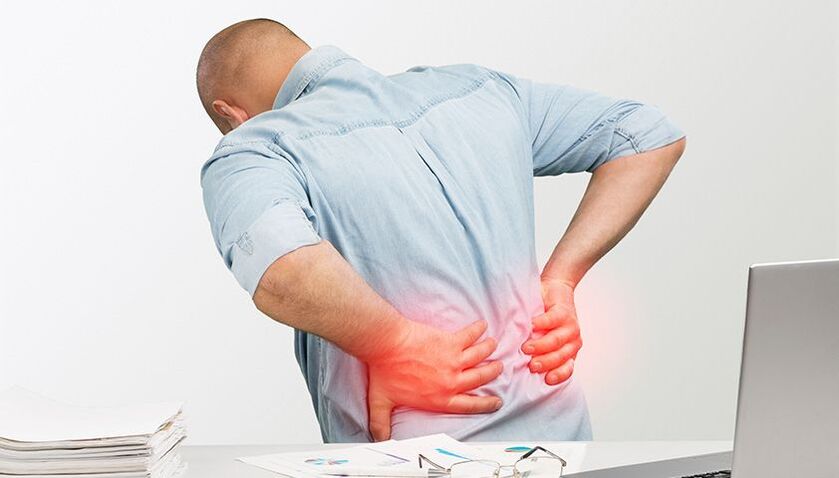
Low back pain is quite common. It can be caused by both ordinary fatigue and serious injuries and pathologies. If the pain is severe or does not go away after rest, it is important to see a doctor to rule out dangerous conditions.
What can pain in the lower back be like?
Pain in the lower back can be sharp or painful, appear suddenly or increase gradually, appear with loads or certain movements (for example, bending over), or persist regardless of what the person is doing.
The pain may be punctual or radiate (that is, spread to other areas). In this case, a person feels pain not only in the back in the lumbar region, but also in other parts of the body, such as the lower abdomen, perineum, leg or buttocks.
Low back pain may include stiffness of motion or muscle spasms. The person may have difficulty bending over or getting up from a lying position, standing up straight, or maintaining posture when walking.
If the pain is caused by a muscle spasm or a pinched nerve, it can be unbearable and even disabling. This pain forces him to stay in bed until he receives medical help.
Why does my lower back hurt?
The most common cause of pain in the lower back is one or another pathology of the musculoskeletal system: sprains, pinching, inflammation. They are often found in men who work with their hands, athletes and young mothers.
In addition, discomfort in the lower back can be a sign of acute or chronic diseases of internal organs. This is because painful impulses can be transmitted along nerve fibers to neighboring regions. In this case, they say that the pain "radiates" to the lower back.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system that cause pain in the lower back.
Most often, low back pain is caused by injuries and pathologies of the musculoskeletal system: sprains of muscles and ligaments, spinal injuries, herniations and protrusions of intervertebral discs, inflammation of the joints and bone diseases.
Deformations and sprains of muscles and ligaments.
These injuries can occur due to awkward movements if a person lifts something very heavy or does not follow safety precautions when handling bulky objects. You can also get injured while playing sports or if you simply sneeze unsuccessfully.

Lower back pain can occur if you lift heavy objects without following safety precautions.
In case of sprains and strains, the pain intensifies during movement and muscle spasms may appear. It may be painful for the person to walk, lean forward, or keep their back straight.
Diagnosis of deformation and sprain of muscles and ligaments is based on data from a physical examination and instrumental studies: ultrasound, X-ray, MRI of the lumbar region. If you suspect a sprain or deformation of muscles or ligaments, you should contact an orthopedic traumatologist.
Treatment involves relieving acute pain and muscle spasms using ice packs, pain relievers, and medications to relieve muscle spasms (muscle relaxants). It is important to let the damaged area rest to allow the tissue to recover; This usually takes about 2 weeks. After this, it is important to start rehabilitation: physiotherapy exercises aimed at restoring muscle function are indicated.
Without treatment, strains and sprains lead to limited mobility: Trying not to injure the damaged area, a person reduces activity, which can lead to weight gain, decreased bone strength, and loss of muscle mass.
spinal injuries
Damage (usually a fracture) to one or more vertebrae occurs as a result of falls, accidents, sports, or domestic injuries. In people with bone density disorders (such as osteoporosis), such damage can be caused by even minor exposures.
Treatment of spinal injuries consists of preventing displacement and further deformation of the intervertebral discs. If the damage is not severe, it is recommended to sleep on a hard surface and limit physical activity. If the damage is significant, surgical methods are used for fixation.
Without treatment, damage to the spinal discs can cause stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal, neurological disorders, including sciatica - pinched nerve fibers that extend from the spine.
Intervertebral disc pathologies.
Intervertebral discs are fibrocartilaginous plates with gelatinous content located between the vertebrae. They act as shock-absorbing cushions for the vertebrae, ensuring their mobility. Discs can detach (bulge) or rupture (herniate), causing severe pain and limiting spinal mobility.
Intervertebral hernias and protrusions can occur in people with weak muscles and excess weight, in those who lead a sedentary lifestyle or lift heavy objects. People who smoke are more susceptible to intervertebral disc pathologies.
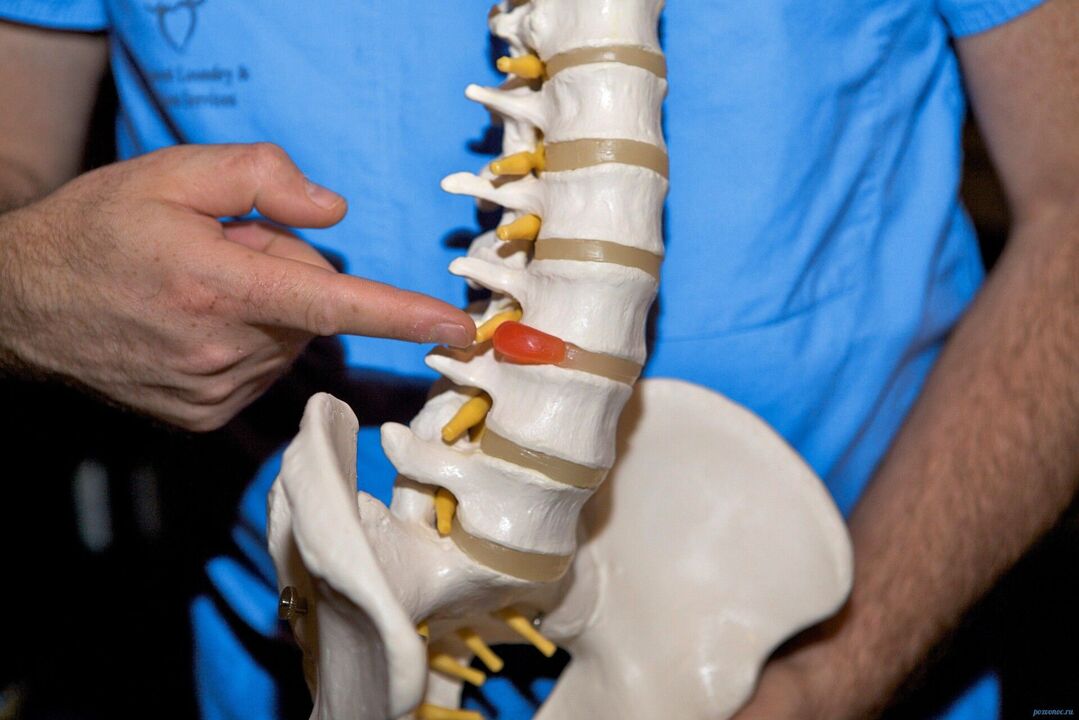
Intervertebral hernia: protrusion of an intervertebral disc into the spinal canal.
Treatment consists of relieving pain and inflammation; Rest, pain relievers, ointments and compresses on the inflamed area are recommended. The doctor may prescribe physical therapy or exercise therapy. In case of moderate damage, the disc can be recovered if the cause of the herniation or protrusion is excluded, for example by strengthening the muscle corset, reducing weight and not placing excessive stress on the spine.
If the pain in your lower back is so severe that it interferes with daily activities, does not go away within 1 to 1. 5 months, or if your symptoms worsen, you should contact your doctor again. In some cases, steroid therapy or even surgery may be necessary. With age, it is possible to develop degenerative diseases of the intervertebral discs: they become flatter and perform a worse shock absorption function, which can also cause pain. In this case, the treatment includes pain relief and general improvement of the body.
Scoliosis of the lumbar spine
Scoliosis (curvature) of the spine is a displacement of the spine to the right or left with respect to the vertical axis. The pathology leads to increased pressure in certain areas of the intervertebral discs and vertebrae, as well as pinching of tissue and nerve fibers. Scoliosis can cause severe pain in the right or left lower back, where most stress is placed, and severely limit spinal mobility.
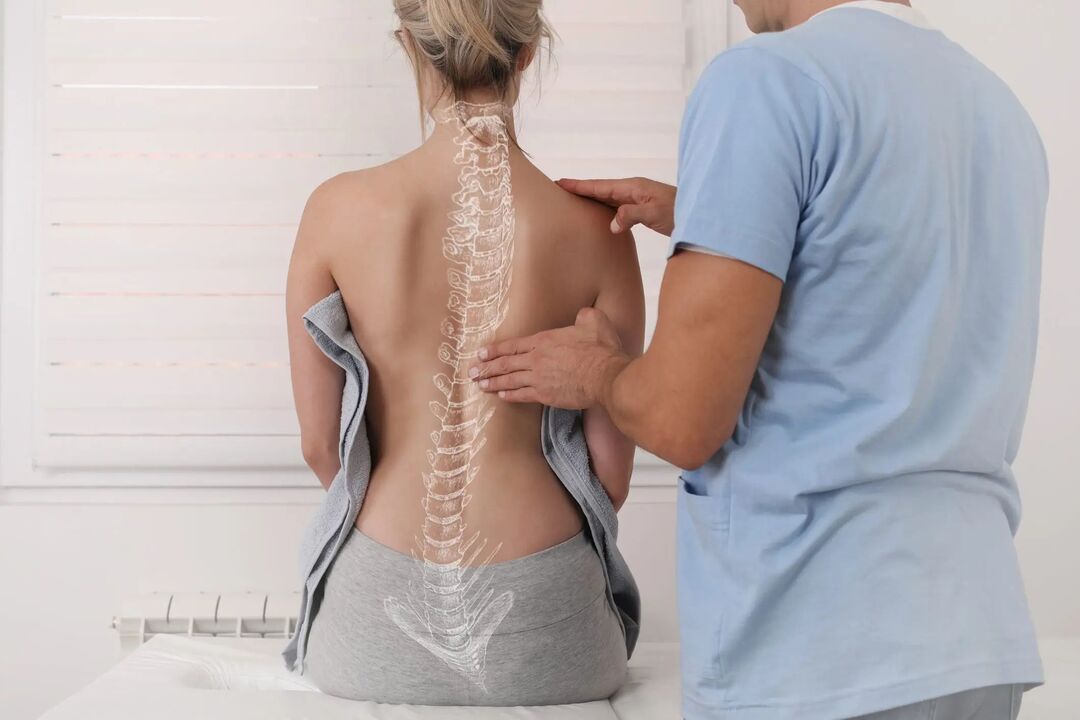
Scoliosis (curvature) of the spine can cause severe pain in the area of the lower back where a lot of stress is exerted.
Scoliosis can occur due to weakening of the muscle corset in the absence of sufficient physical activity, a sedentary lifestyle (in schoolchildren, office workers). In this case, it is difficult for the muscles to maintain the physiological position of the back and curvatures are formed.
Treatment involves the introduction of balanced physical activity (physiotherapy, swimming), massage and manual therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures to strengthen muscles, such as electrical stimulation. In case of serious injuries, it is recommended to use a corset, which helps maintain the correct position of the spine.
Arthritis and osteoarthritis
Inflammation and degenerative processes in the joints of the spine can also cause severe lower back pain. There are many forms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis (damage to cartilage and adjacent tissues), ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis - damage to the joints of the spine, leading to fusion of the vertebrae).
Arthritis can be caused by natural aging, genetic predisposition or autoimmune diseases.
Treatment of arthritis, depending on its form, may include the use of steroidal and non-steroidal analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, electrophoresis), therapeutic massages and physiotherapy.
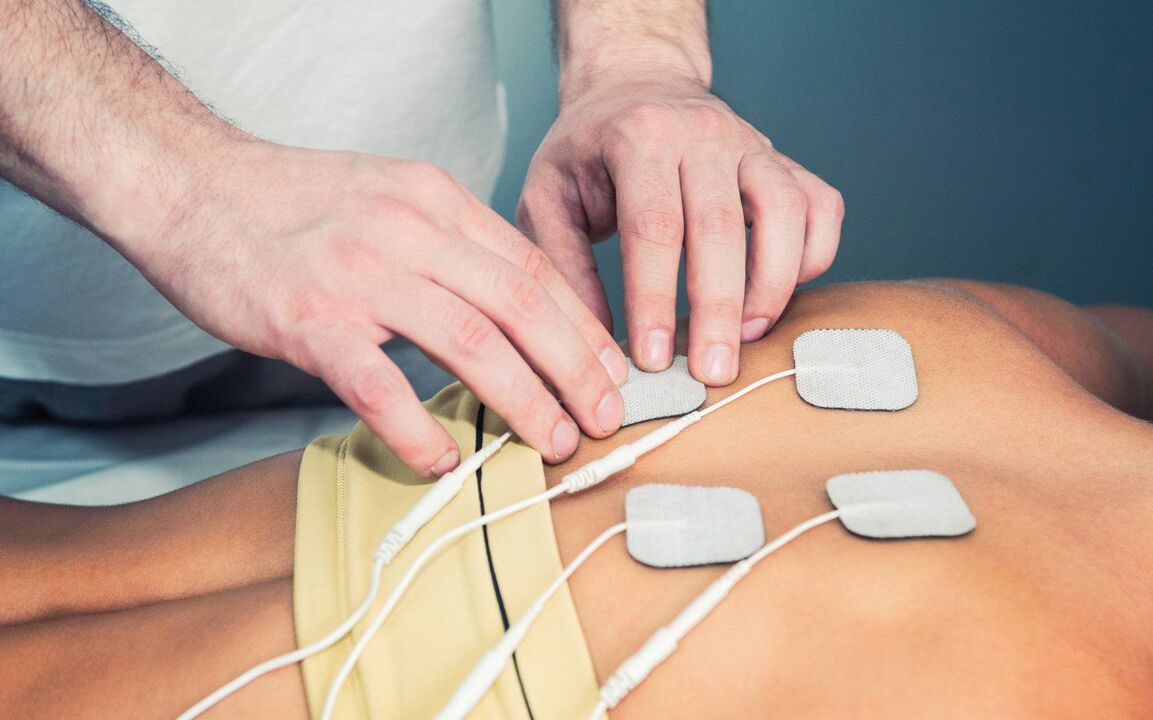
Physiotherapeutic procedures help relieve pain due to joint pathologies.
spondylolisthesis
The displacement of a vertebra with respect to the spinal column (spondylolisthesis) occurs as a result of an injury or degenerative processes in the spine. Pathology occurs in athletes, elderly people, or people with a hereditary predisposition to bone diseases (for example, osteoporosis, a bone density disorder). Spondylolisthesis can cause severe pain in the lower back, buttocks, and legs, and cause leg cramps or weakness.
The treatment consists of relieving the pain and inflammation that occurs due to the compression of neighboring tissues by the vertebra. Depending on the severity of the pain syndrome, the doctor may prescribe non-hormonal pain relievers in tablets or corticosteroid injections. At the same time, physiotherapeutic procedures and exercise therapy are prescribed to strengthen the muscles and restore the position of the vertebrae. If spondylolisthesis is accompanied by very severe pain, surgical treatment is used.
In traumatic and non-infectious pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, pain in the lower back usually subsides or decreases when the person adopts a comfortable position.
If spondylolisthesis is accompanied by severe pain, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroid injections.
Infectious diseases of the spine.
Inflammation of bone tissue (osteomyelitis) and inflammation of the intervertebral disc (discitis) can cause severe low back pain. These pathologies are usually secondary in nature, that is, they arise as a complication of inflammation of other organs (the infection enters the tissues through the bloodstream).
Treatment involves hospitalization, lasting up to 1 month, and then requires rehabilitation, which lasts 6 to 12 months.
Tumor diseases of the spine.
Neoplasms can develop under the influence of hereditary or external factors (for example, radiation), but most often they appear as repeated foci (metastases) in cancer of other organs: lungs, mammary glands, prostate, thyroid gland and kidneys .
One of the most characteristic symptoms of tumor pathologies is pain that does not subside when changing position or after rest. Symptoms such as numbness, partial paralysis, uncontrolled urination and a sharp increase in body temperature with chills are also possible. Without treatment, symptoms worsen.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the type of tumor, its location and symptoms and may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgical removal of the tumors. Pain relief is achieved with non-hormonal drugs or steroids. To stabilize your spine, your doctor may prescribe the use of a corset.

The orthopedic corset helps stabilize the spine.
Diseases of internal organs that cause pain in the lower back.
Low back pain can occur with diseases not associated with pathologies of the spine and adjacent tissues. Acute or painful, it can accompany inflammation of internal organs: pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, aneurysm of the abdominal aorta. In women, pain in the lower back can develop due to gynecological pathologies.
Urolithiasis disease
A disease in which stones form in the kidneys and bladder, hard formations of the sediment of the chemical components of urine. Low back pain is one of the main signs of pathology. Depending on the size and location, kidney stones can cause a dull, aching pain that comes and goes periodically, or a very sharp pain that does not go away on its own and requires emergency medical attention.
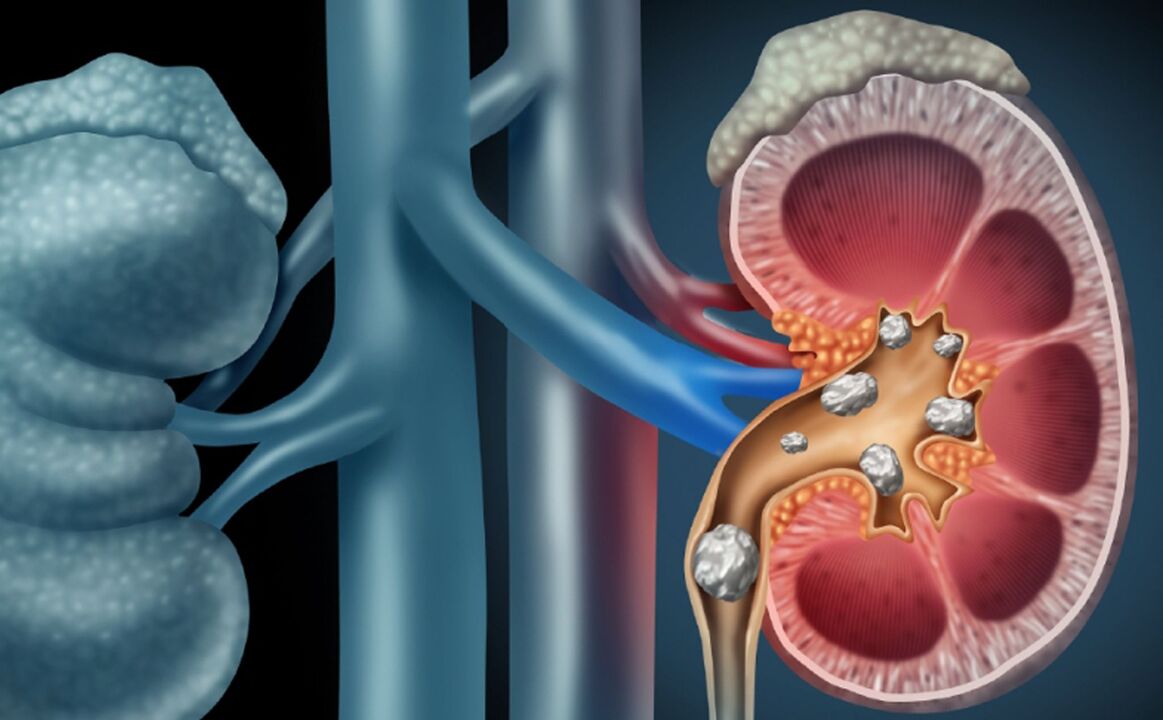
Urolithiasis - the formation of stones in the kidneys and bladder.
If you suspect kidney stones, you should consult a urologist or nephrologist. The doctor will prescribe instrumental tests and studies (ultrasound, X-ray examination, computed tomography, including with the use of a contrast agent) to make a diagnosis and choose treatment tactics.
Treatment is prescribed taking into account the size, nature, location of the stones and other factors. If the stone is small (5 to 10 mm) and there are no other indications for its surgical removal, pharmacological treatment is used. If there is no positive dynamics within a month, removal by surgical or non-invasive methods is recommended.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
A weakening of the walls of the abdominal aorta (aneurysm) can lead to life-threatening conditions such as aortic rupture and intra-abdominal hemorrhage. As a rule, pathology occurs in older people: the risk group includes men over 65 years old and women over 70 years old, including smokers, those who suffer from vascular diseases (high blood pressure), who have previously had aneurysms or who have had a hereditary predisposition to them.
Pain in the lower back due to an abdominal aortic aneurysm does not go away over time and may be accompanied by pain in the abdomen and legs.
If an aneurysm is suspected, an abdominal ultrasound and CT scan are prescribed.
Treatment depends on the size of the aneurysm. Small changes require follow-up with twice-yearly instrumental examinations and lifestyle adjustments. Large ones (more than 5 cm, with high risk of rupture) are an indication for abdominal or minimally invasive surgery.
How to prevent lower back pain
Since low back pain is usually caused by a traumatic injury to the muscles, fascia, joints or bones, the main recommendation for prevention is to follow safety precautions and maintain a strong muscle corset, as well as healthy bones and joints. .
Prevention of sprains and microtrauma of the lumbar area:
- a varied diet that includes the vitamins and minerals necessary to maintain healthy bone, muscle and joint tissues;
- keep a healthy weight;
- regular physical activity: exercises to prevent low back pain should include strength exercises to develop muscle structure, stretching to relieve muscle tension and spasms, and cardiovascular training to maintain blood supply and tissue nutrition;
- compliance with safety precautions when playing sports; For example, the first classes in the gym must be supervised by a qualified trainer;
- Compliance with home safety precautions: Many injuries can be avoided by wearing comfortable shoes, holding onto stair railings, and taking your time when it's slippery outside;
- observe safety precautions when lifting heavy objects: the load on the spine will be less if you approach the object as close as possible (do not reach for it) and when lifting objects from the floor, bend your legs instead of bending your body.

Yoga and Pilates classes help relieve spasms and tension in the lower back
Smoking impairs blood circulation and impairs tissue nutrition, increasing the risk of damage and injuries.
What to do if your lower back hurts
If your lower back hurts, the reasons may be different, which means that the treatment tactics will also be different.
In case of severe physical fatigue, it is necessary to rest your back; perhaps this will be enough for the muscles to recover and regain spinal mobility.
If the pain does not disappear within 1-2 days or is very severe, a doctor should be consulted. While waiting for a doctor, you can try to relieve acute pain with pain relievers.
At the appointment, the doctor will perform an examination, determine the cause of the pain, and give treatment recommendations. This will help eliminate dangerous conditions and prevent the development of complications.
Warming (lumbar pepper patch, hot water bottle, sauna) is contraindicated for inflammation, but can relieve acute pain in the lower back if it is caused by muscle fatigue or a pinched nerve. These methods can only be used after consulting a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact if I have low back pain?
If you suspect pathology of the musculoskeletal system, you should contact a neurologist and orthopedic traumatologist.
Diagnosis is made by physical examination and by instrumental methods: MRI therapy, CT, X-ray and ultrasound. It is also possible to prescribe a myelogram (an X-ray study or computed tomography with a contrast agent injected into the spinal canal) and electromyography - a study that makes it possible to assess the state of nerve and muscle fibers.
If you suspect kidney disease, you should consult a urologist, nephrologist or therapist. The doctor will analyze the complaints and conduct a physical examination, and then prescribe instrumental and laboratory tests to clarify the diagnosis.
From blood and urine tests, the doctor will be able to determine if there is inflammation in the organs of the urinary system, and ultrasound and X-ray studies will help visualize the organs, determine the cause of pain and choose the most effective treatment. tactic.
If the origin of pain in the lower back is unclear, a general practitioner or therapist should be consulted.
The doctor will collect an anamnesis (medical history), analyze hereditary risks, conduct a physical examination and prescribe tests that will identify inflammatory processes or disorders in the functioning of internal organs.
A general blood test helps to identify the inflammatory process.
If necessary, the doctor will refer you to instrumental studies (ultrasound, X-ray, MRI) or recommend contacting a specialist for further diagnosis and treatment.



















